 Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Myofascial Pain Syndrome
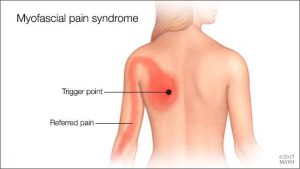
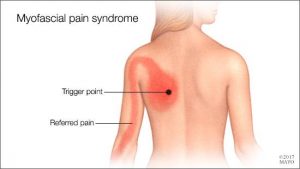
Myofascial pain syndrome is where pressure on sensitive points within your muscles (trigger points) causes pain and sometimes refers pain to seemingly unrelated parts of your body. It can occur after a muscle has been contracted repetitively ie. repetitive motions used in jobs or hobbies or by stress-related muscle tension. While nearly everyone has experienced muscle tension pain at some point, the discomfort associated with myofascial pain syndrome persists or worsens. There is no laboratory, radiographic or other diagnostic tests to prove the diagnosis of myofascial pain syndrome so it is considered a “subjective” diagnosis. Myofascial trigger points do not always cause pain. Sometimes they can lie dormant or inactive within a muscle for months or even years. Trigger points can often be identified by a skilled therapist working through your muscles with deep tissue massage. They feel like little knots deep within the muscles which when pressed are extremely tender.
Fascia is the body’s connective tissue. It is a head to toe, all-encompassing and interwoven system of fibrous connective tissue found throughout the body. Your fascia provides a framework that helps support and protect individual muscle groups, organs, and the entire body as a unit. It is the same as that cling film, elastic type structure that surrounds a joint of meat, helping hold it together when the outer skin is removed.
This fascia in itself can also contribute to ”myofascial pain” syndrome. Injury, illness, stress, aging and repetitive use, can cause the fascia to shorten, thicken and become more unyielding . All the nerves and blood vessels run through the fascia. Therefore, if this connective tissue is tight, the associated tissues will have poor nutrient exchange. This exacerbates any painful situation because toxic metabolic waste products build up which often further aggravate pain receptors. This can create a vicious cycle, leading to increased muscle tension and further thickening and hardening of the fascia, which in turn further limits mobility.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of myofascial pain syndrome may include:
- Deep, aching pain in a muscle
- Pain that persists or worsens
- A tender knot in a muscle
- Difficulty sleeping due to pain
- Spasm in the area
The most commonly affected muscle groups include those of the neck, shoulders, upper & lower back. Generally one side of the body is more affected than the other. It is common for patients with myofascial pain syndrome to have poor sleep patterns. This is associated with feeling unrested after a nights ”sleep” and daytime tiredness . Stiffness after inactivity is also a common feature.
Treatment
Myofascial pain can often benefit greatly from ”proper skilled deep tissue massage”, and trigger point release, both manual and with dry needling techniques. The fascia can also be stretched and worked out during the massage. This is also one of the benefits of a stretching program when incorporated into your exercise routine. It helps keep prevent the fascia from tightening up because you are continually stretching it out.
During treatment for myofascial pain it is important that the patients reduce their stress levels, if this is a contributing factor to the condition. Exercises prescribed by a physio may also help, along with improving ones sleep patterns. In severe, chronic cases, medications may be needed to aid recovery.
Often trials of different medications are used to find the best treatment for a particular patient. For example, trazodone or amitriptyline may be used at bedtime to improve sleep as well as relieve pain; cyclobenzaprine or orphenadrine can also be used to relax muscles and aid sleep; and antidepressants such as sertraline, fluoxetine(prozac), duloxetine, can be used to control pain, as can lyrica and gabapentin. Medications have side effects, so are added as a last resort in chronic cases showing little improvement with physio alone. They should only be taken under a doctors supervision.
Physiotherapists Tralee : Phone 0867700191
 Myofascial Pain Syndrome
Myofascial Pain Syndrome